Erneuerbare Fernwärme 2020
Erneuerbare Fernwärme 2020
Das multifunktionale Fernwärmenetz als Wärmedrehscheibe
Projektthema
- Speicher
- Solarthermie
- Energieversorgung
- Nah- und Fernwärme
Aufgabe
- Beratung
- Studie
- Wissenstransfer
- Entwicklung
- Forschung
- Pilotprojekte
Förderung
- Öffentliche Hand
Projektdauer
10/2017 – 09/2022 (5 Jahre)
Gesamtbudget
3,8 Mio. EUR
Projektbeschreibung
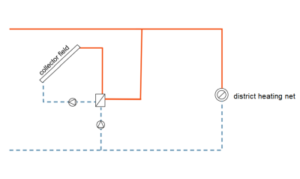
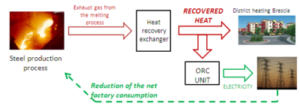
Bis zum Jahr 2022 soll der Anteil CO2-neutraler Wärme an der Fernwärmeversorgung der Stadt Hennigsdorf von 50 auf über 80 % erhöht werden. Dafür wird die Abwärme des örtlichen Stahlwerks, Solarthermie und Power-to-Heat aus regenerativem Überschussstrom in das Wärmenetz eingebunden und ein Multifunktions-Wärmespeicher realisiert.
Auftraggeber
BMWi
Partner
- Kraftwerks- und Projektentwicklungsgesellschaft mbH & Co KG
- Stadtwerke Hennigsdorf GmbH
- Ruppin Consult GmbH
- Steinbeis Forschungsinstitut Solites
- tetra ingenieure GmbH
Ziel
Mit einem Klimaschutzrahmenkonzept wurde im Jahr 2015 die nachhaltige Fernwärmeversorgung der Stadt Hennigsdorf beschlossen. Der CO2-neutrale und regenerative Anteil an der Wärmeversorgung soll mit den folgenden Schritten auf über 80 % erhöht werden:
- Abwärmenutzung aus dem örtlichen Stahlwerk
- Ausbau der solarthermischen Wärmeerzeugung (zentral und dezentral)
- Power-to-Heat aus regenerativem Überschussstrom (Vorhaben WindNODE Schaufenster der Energiewende)
- Erschließung aller Optimierungspotentiale in den Abnehmeranlagen und im Fernwärmenetz
- Abbau von Altanlagen, die mit Heizöl oder Anthrazit befeuert werden
- Errichtung eines Multifunktions-Wärmespeichers mit 22.000 m³ und eines Pufferspeichers mit 1.000 m³ Wasservolumen
Umsetzung
In dem vorhergehenden durch das BMWi geförderten Projekt “Wärmedrehscheibe Phase 1” wurde ein Konzept mit den wissenschaftlich-technischen Grundlagen für die Optimierung der Fernwärmeversorgung und den Ausbau einer nahezu vollständig CO2-neutralen Versorgung erarbeitet. Dieses Konzept wird nun durch das Konsortium schrittweise in die konkrete Planung überführt und mit ausführenden Firmen umgesetzt. Dabei werden in dem Verbundvorhaben die Umsetzung der innovativen technischen Anlagen und Baumaßnahmen einerseits und die wissenschaftliche Begleitung andererseits gefördert.
Solites hat die Rolle der wissenschaftlichen Begleitung und Evaluierung und erarbeitet darüber hinaus am Beispiel der Stadt Hennigsdorf allgemeingültige wissenschaftliche Grundlagen, die in der Folge auf die Fernwärmeversorgung anderer Städte übertragen werden können.
Ergebnisse
Im Frühsommer 2019 wurde die Nutzung der Abwärme aus dem Stahlwerk erfolgreich realisiert. Dazu wurde ein neues Heizwerk “Nord 2” gebaut, über das die Abwärme in das Fernwärmenetz transportiert wird.

Downloads und Links
www.swh-online.de/erneuerbare-fernwaerme-2020/
Kontakt
Dirk Mangold
mangold@solites.de
Magdalena Berberich
berberich@solites.de
Dieses Projekt wird gefördert durch

Die alleinige Verantwortung für den Inhalt dieser Website liegt bei den Autoren. Sie gibt nicht unbedingt die Meinung der Fördermittelgeber wieder. Weder die Autoren noch die Fördermittelgeber übernehmen Verantwortung für jegliche Verwendung der darin enthaltenen Informationen.